UGI Endoscopy
Upper GI (gastrointestinal) endoscopy, also known as esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)About UGI Endoscopy
Upper GI (gastrointestinal) endoscopy, also known as esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or simply upper endoscopy, is a procedure that allows doctors to examine the inner lining of your upper digestive tract. This includes:
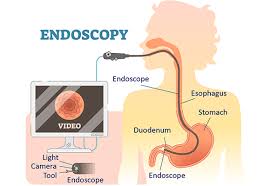
- Esophagus: The muscular tube that connects your mouth to your stomach.
- Stomach: The muscular sac that stores and breaks down food.
- Duodenum: The first part of your small intestine.
Here's a breakdown of what an upper GI endoscopy typically involves:
Purposes of a UGI Endoscopy:
-
Diagnosis: An upper GI endoscopy is a versatile tool used to diagnose a variety of conditions affecting the upper digestive system, such as:
- Heartburn (GERD)
- Stomach ulcers
- Esophageal inflammation (esophagitis)
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Stomach bleeding
- Celiac disease
- Crohn's disease (if it affects the upper intestine)
- Growths or tumors
-
Treatment: During an upper GI endoscopy, doctors can sometimes perform certain procedures to treat some conditions, such as:
- Stopping bleeding ulcers
- Removing polyps (abnormal growths)
- Opening narrowed passages (strictures)
Procedure:
- Preparation: You will likely need to fast for several hours before the procedure to ensure your stomach is empty. You may also be asked to stop taking certain medications that could interfere with the procedure.
- Process: During the endoscopy, you will be given medication to help you relax and feel drowsy. You will lie on your side on an examination table. The doctor will insert a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope into your mouth and gently guide it down your esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The endoscope has a tiny light and camera at the tip, which allows the doctor to see the lining of your upper digestive tract on a monitor.
- Discomfort: You may experience some gagging or discomfort during the insertion of the endoscope. The entire procedure typically takes 15-30 minutes.
Benefits of a UGI Endoscopy:
- Minimally invasive: Upper GI endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure compared to traditional surgery.
- Accurate diagnosis: It allows for a direct visualization of the upper digestive tract, aiding in accurate diagnosis.
- Treatment options: In some cases, it can be used for therapeutic purposes as well.
Things to Consider:
- Risks: While uncommon, there are potential risks associated with upper GI endoscopy, such as bleeding or infection at the insertion site.
- Alternatives: Depending on the suspected condition, your doctor might recommend other tests like X-rays or a CT scan as initial investigations.
Overall, upper GI endoscopy is a safe and valuable tool for diagnosing and treating various conditions affecting the upper digestive tract. If your doctor recommends an upper GI endoscopy, discuss any concerns you may have and ask about the reasons behind the recommendation.