COLONOSCOPY
colonoscopyAbout COLONOSCOPY
A colonoscopy is a medical procedure that allows a doctor to examine the inner lining of your entire large intestine (colon) and rectum for abnormalities such as polyps or cancer.It is a safe and effective way to screen for and prevent colon cancer, the second leading cause of cancer death in the United States for both men and women.
pen_spark
Colonoscopy procedure
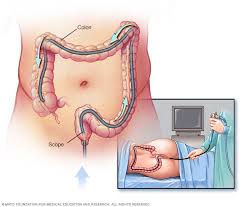
How is a colonoscopy performed?
A colonoscopy is usually performed by a gastroenterologist, a doctor who specializes in the digestive system. The procedure is typically done on an outpatient basis, which means you won't have to stay overnight in the hospital.
Here's a general breakdown of the steps involved in a colonoscopy:
- Preparation: The day before the colonoscopy, you will need to clear your bowels with a laxative or enema. This is important to ensure that your colon is clean and free of stool so that the doctor can get a good view of the lining. You will also need to restrict your diet to clear liquids.
- During the procedure: During the colonoscopy, you will lie on your left side on an examination table. You will be given medication to help you relax and feel drowsy. The doctor will then insert a long, thin, flexible tube called a colonoscope into your rectum and gently guide it through your colon. The colonoscope is equipped with a tiny light and camera that allows the doctor to see the inside of your colon on a monitor.
- Biopsy: If the doctor sees any abnormal areas during the colonoscopy, they may take a small tissue sample (biopsy) for further examination under a microscope. This is a painless procedure.
- Polyp removal: If the doctor finds any polyps during the colonoscopy, they can usually be removed during the procedure. Polyps are small growths on the lining of the colon that can sometimes turn into cancer. Removing polyps can help prevent colon cancer.
- Recovery: After the colonoscopy, you will be taken to a recovery area where you can rest until the medication wears off. You may feel groggy or bloated for a short time after the procedure. You will be able to go home once you are feeling well enough.
Benefits of a colonoscopy:
- Colonoscopy is an effective way to screen for and prevent colon cancer.
- It can also be used to diagnose other digestive problems, such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
- Colonoscopy is a safe procedure with a low risk of complications.
Who should get a colonoscopy?
The American Cancer Society recommends that all adults starting at age 45 should get screened for colon cancer. People with a family history of colon cancer or certain risk factors may need to start screening earlier or be screened more often.
Risks of a colonoscopy:
Colonoscopy is a safe procedure, but there are some potential risks, such as:
- Bleeding from the biopsy site
- Infection
- Tearing of the colon (perforation)
These risks are rare, and the benefits of colonoscopy far outweigh the risks.